Skin model to target sensitive skin
Sensitive skin is characterized by several phenomena: a defect in the cutaneous barrier, as well as increased inflammation. This result in skin dryness, irritation, an excessive reaction to external stimuli and a feeling of discomfort. Nearly 60% of the population describe themselves as having sensitive skin.
To address this issue, Syntivia has validated an ex-vivo model close to sensitive skin. It will enable us to test ingredients and formulas under development for fragile skin.
A human skin model to target sensitive skin
We have chosen the skin explant as our favoured model. As the explant is obtained from surgically derived human skin, it is the most representative of the complexity of human skin.
We are working on a ex-vivo skin model with a barrier defect, dehydration and expressing the main markers of sensitive skin. The skin is first stripped and then exposed to a pro-inflammatory treatment, thus presenting a phenotype similar to that of sensitive skin. (figure 1).
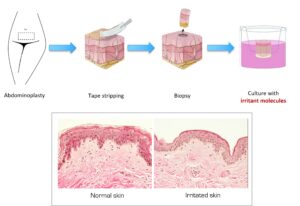
Figure 1: Human skin explant after stripping and exposition to irritant molecules to mimic fragile skin phenotype.
Damage to the barrier function and loss of moisture are recurrent cutaneous phenomena in fragile or sensitive skin, and must be prevented.
Impaired skin barrier:
After 7 days of treatment, we measure the thickness and quality of the reconstructed stratum corneum.
The stratum corneum gradually re-forms but shows an immature appearance or may show parakeratosis after 7 days.
In addition, main markers of keratinocyte differenciation in the stratum corneum after immunolabelling (figure 2):
- Filaggrin: crucial pour l’agrégation des filaments de kératine dans les cellules de l’épiderme pour la maturation
- Loricrin: major protein of the horny envelope
- Ceramides: essential lipids in the stratum corneum
- Involucrin (not shown): structural protein involved in the formation of the horny envelope by binding to cell membrane lipids.
The expression of these markers decrease in our model and can be reactivated.
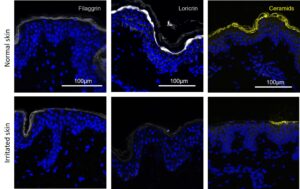
Figure 2: Stratum corneum markers detected by immunofluorescence in healthy and artificially irritated skin after 7 days of culture.
Dehydration :
Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) significantly increases while glycerol skin content decreases (figure 3). Indeed, a low concentration of glycerol may lead to decrease the water content of both epidermal and dermal compartments. The structural changes to the skin that could result would lead to a change in cutaneous micro-relief and an increased TEWL.
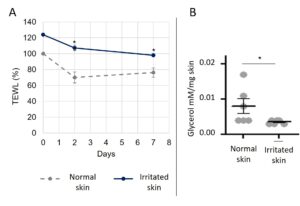
Figure 3: Singinficant decrease in Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL) (A) and Glycerol content (B) in healthy and artificially irritated skin during 7 days of culture.
Inflammation and Neuroinflammation mediators:
The model is characterized by the production of inflammation mediators associated with non-specific inflammation but also TRPV1 associated to neuro-inflammation (figure 4):
- Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα)
- Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) : particularly associated with sensitive skin.
- Transient Receptor Potential, Vanilloid Family 1 (TRPV1)
TRPV1 expression increases in the skin model and may contribute to activation of inflammation mediators. This ion receptor plays an important role in pain perception and thermoregulation. In people with sensitive skin, TRPV1 may be more reactive or expressed in greater quantities, leading to increased sensitivity to external stimuli.
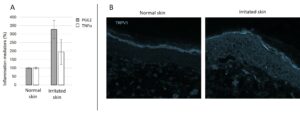
Figure 5: Activation of the expression of inflammation mediators TNFα and PGE2 (A) and activation of the expression of TRPV1(B) in healthy and artificially irritated skin during 7 days of culture.
EVALUATION OF SOOTHING PRODUCTS
To conclude, this ex vivo human skin models are ideal to study the effect of soothing compounds and formula dedicated to sensitive skins. This will not only optimize the chances of success in clinical trials, but also identify the product’s biological pathways. Other readouts and markers can be analyzed on this model.
Don’t hesitate to contact us for more information on our human skin models and product testing. You can also share your projects with us so that we can set up a study adapted to your needs.