Syntivia combines transparent skin model and 3D skin imaging to study aging
Syntivia recently attended the Skin Physiology International Meeting in the Vichy Palais des Congrès (France) on November 17th and 18th, 2016 to present an innovative method to study effects on human skin. In a collaborative project with the Institute of Advanced Life Science Technology (ITAV) in Toulouse, Syntivia associates a transparent skin model and high-tech 3D imaging microscopy for an in-depth study of human skin and the mechanisms of aging.
 The work was presented by Sophie Abadie, our brilliant PhD student. Her goal is to develop a human skin model to evaluate the activity of dermo-cosmetic products designed to prevent premature aging. The model uses ex-vivo human skin explants that are UVA-irradiated to mimic the skin’s natural exposure to the sun.
The work was presented by Sophie Abadie, our brilliant PhD student. Her goal is to develop a human skin model to evaluate the activity of dermo-cosmetic products designed to prevent premature aging. The model uses ex-vivo human skin explants that are UVA-irradiated to mimic the skin’s natural exposure to the sun.
Transparent skin to observe 3D structures
To observe all potential activities within the skin model, the human skin samples were made transparent using a special transparization technique. The resulting model was then subjected to high-tech 3D skin imaging. The Selective Plan Illumination Microscope (SPIM) allows to use Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy (LSFM) to explore morphological changes at sub-cellular level in 3D.
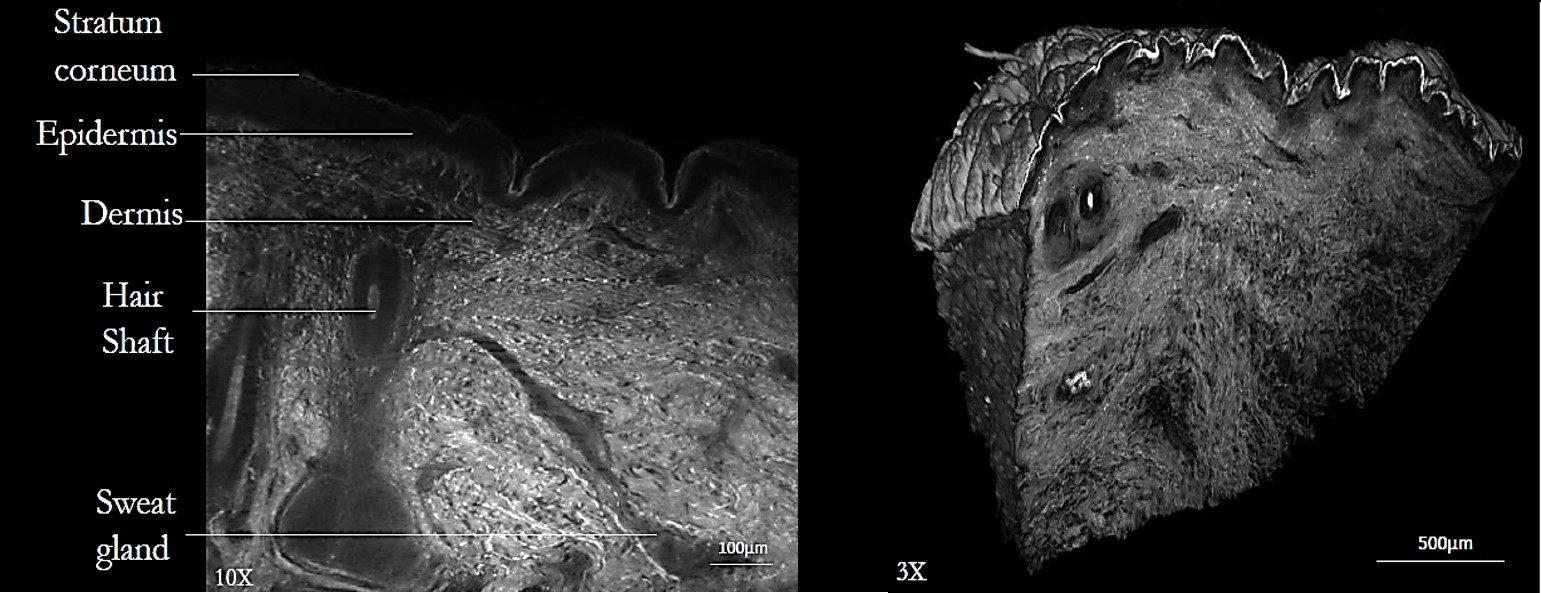 3D skin imaging of a human skin biopsy observed by LSFM to study changes in the main skin compartments: epidermis thickness, dermo-epidermal junction structure and dermis cohesion.
3D skin imaging of a human skin biopsy observed by LSFM to study changes in the main skin compartments: epidermis thickness, dermo-epidermal junction structure and dermis cohesion.
Copyright Abadie S, Colombelli J, Jardet C, Descargues P, Bedos P, Ducommun B, Rouquette J
The advantage of this technique is its extremely fast optical sectioning, which is performed directly on the biopsy with a good resolution. In combination with transparent biopsies, this 3D skin imaging method enables us to obtain images at several millimeters of depth for 3D reconstruction and analysis.
This high-tech project is a huge step forward towards reliable scientific imaging in order to efficiently demonstrate the activity of cosmetic active ingredients and formulas.
The full results of this study will be published shortly. In the meantime, don’t hesitate to contact us for more information on our testing procedures.